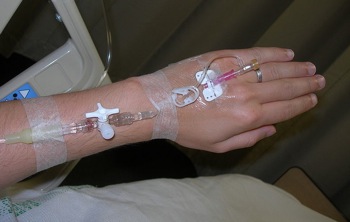
used with permission, Michael Berry
Peripheral venous access, or intravenous (IV) access, is commonly used to administer fluids, medications, or blood.
IV therapy is one of the fastest routes of providing medication, and is the most effective means of providing fluids during periods of dehydration or hemodynamic instability.
Indications
Peripheral IVs are used to:
- administer medications, IV fluids, blood, or parenteral nutrition
- maintain access for the above in a potentially unstable patient
- sample venous blood (when necessary)
Contraindications
The following contraindications all relate to the site chosen rather than the procedure itself.
- existing skin infection in intended IV site
- venous thrombosis proximal to intended site
- arterial-venous shunt (i.e. for hemodialysis) in extremity
- lymphatic obstruction (i.e. following axillary node dissection) in extremity
Procedure
Choosing Catheter Size
Teflon/Plastic catheters are the most common type of catheter used. They range in size from 14 – 25g.
- 22-25g – pediatric applications or occasionally in adults with very small veins
- 20g – standard, multipurpose adult IV
- 18g – suitable for higher flow rates in adults and for routine administration of blood products
- 14 – 16g – large (painful) catheters reserved for situations where volume resuscitation is needed or anticipated. i.e. hypovolemic shock, GI bleeding, Some preoperative surgical cases
Butterfly Catheters are generally used only in pediatrics and for very short-term venous access, as they tend to perforate veins easily and are more prone to infection. Sizes 20 – 25g.
Safety IV catheter systems are increasingly used to reduce needle stick injuries by encasing the entire needle within a guard.
Choosing the Site
Upper extremities are generally preferred to lower as they are more convenient for staff and patient and pose lesser risk of infection, phlebitis and deep vein thrombosis.
Preferred sites are dorsal hand and volar forearm, in the non-dominant arm if possible. Try to pick a long straight section of vein or a bifurcation. Start as far distal on the arm as possible – if you miss you can try more proximally without getting leaks from previous sites.
If the IV is being placed to resuscitate a patient, veins within the antecubital fossa (the inside of the elbow) should be considered, given their relatively bigger size.
Sites to Avoid
- joints – more difficult to stop the IV from kinking or infiltrating when the joint is flexed
- infected skin/cellulitis – for obvious reasons.
- extremities with arteriovenous fistulas (ie hemodialysis patients)
- traumatized extremities – veins may be interrupted or occluded proximally
- extremities with venous insufficiency i.e. post mastectomy
- paretic limbs i.e. stroke, spinal cord injury
Materials Required
- povidone – Iodine Swabs
- alcohol Swabs
- tourniquet – Velcro, Elastic or BP Cuff
- IV Catheter (Hopefully just one)
- normal saline Lock
- 10 cc syringe with normal saline for flushing
- tape
- transparent Dressing (i.e. Tegaderm, Opsite)
- gloves
- IV infusion setup
- local Anaesthetic i.e. 1 – 2 % Plain Xylocaine in Tuberculin Syringe
- incontinence Pad – for under the patient’s arm so the area nurse won’t curse you
- incontinence Pad – for yourself if first try with an IV (Optional)
Accessing the Vein
© 2006-2007. PocketSnips (http://www.pocketsnips.org).
Video – Intravenous line insertion. Not a substitute for medical advice.
Explain the procedure to the patient and why it is necessary- obtain verbal consent.
Get everything ready – open packages, tear your pieces of tape etc.
minimal standard (Universal) precautions for IV starts is gloves.
Ensure the patient is comfortable – lying or sitting.
Prepare normal saline lock by cleaning the port with an alcohol swab and priming it with sterile normal saline flush solution. Leave the saline flush syringe attached.
Apply the tourniquet 5 – 10 cm proximal to the chosen site. If using a BP cuff inflate it to ~ 15 mm Hg below arterial systolic pressure.
Prep the skin with Povidone – Iodine starting over the site and circling outwards. Follow this with an alcohol swab in the same fashion. If you choose to use local anaesthesia, raise a small intradermal weal of Xylocaine over the site.
Using your non-dominant hand, hold the patient’s extremity and gently pull the skin taught over the vein. Using the safety IV catheter insert the needle bevel upwards, parallel to the skin surface.
Push the needle into the vein until you feel a pop and blood appears in the flash chamber of the IV Cannula. While holding the needle stationary, advance the cannula into the vein by placing the forefinger of your dominate hand, or the thumb of your non dominate hand, against the push-off tab. Pull the needle back into the needle guard until it clicks.
The needle is now encased in the needle guard to help prevent needle stick injuries.
Remove the tourniquet from the patient’s arm.
Attach the primed Normal Saline lock and flush it with 1-3 mls of Normal saline flush solution using the positive pressure technique (the saline injected via a syringe at the same time as the syringe is being removed).
Cover the site with a sterile transparent dressing.
Swab the top of the Normal saline lock again and connect the primed IV tubing. Observe for fluid flow and continue to watch for swelling.
Tape the tubing in place. Properly dispose of sharps, gloves etc
Troubleshooting
Vein Blows or IV solution infiltrates out of vein – Remove it. Apply firm pressure. Try the other arm or more proximal site.
Spider veins (too small) – Dilate veins with warm moist washcloth, gentle tapping, hanging over side of bed (the arm). Some advocate 0.5 cm of nitroglycerine ointment over site.
IV won’t run – Make sure cannula in vein, tourniquet is off, drip valve is open, IV solution bag is elevated. Make sure the drip chamber is not too full. May try withdrawing cannula by few mm in case it’s up against a venous valve.
Air in IV Line – Wind IV tubing around tightly around barrel of a pen, pushing air back into IV bag Or Aspirate air using needle and syringe in the distal injection port.
Complications
Hematoma – generally caused by passing the catheter through the back wall of the vein. Remove catheter and apply local pressure for 5 – 10 minutes.
Extravasation – recognized by local swelling at the IV site. Majority of extravasations are benign and treated by removing the catheter and applying local pressure.
Extravasation Necrosis – occurs secondary to extravasation of hypertonic solutions (D50W, 10 % CaCl, TPN, etc), toxic substances (chemotherapy, contrast dye) or vasoactive substances (epinephrine, dopamine). Accordingly, these are usually diluted or given centrally. If necrosis occurs, discontinue the infusion immediately and consult the pharmacy – some of these substances have specific treatments to reduce the risk of tissue necrosis.
Irritative Phlebitis – recognized by erythema at the site and possibly along the path of the vein. The majority is caused by irritation of the vein by the catheter or infused substances. Irritating substances may be diluted to reduce this risk. Treatment is removal of the catheter, local heat application and sometimes anti-inflammatories.
Infectious Thrombophlebitis – sometimes difficult to distinguish from irritative phlebitis – look for erythema and tenderness proximally along the vein; may be associated with fever. Usually caused by invasion of skin organisms such as Staph. Aureus or Staph. Epidermidis. Aseptic technique and a policy of changing IV sites every 2 – 3 days will reduce the risk. Treatment is by removal of the catheter, local heat and anti-staphylococcal antibiotics
Embolization – uncommon problem unless solutions are being infused under pressure. Small bubbles in a line are not dangerous but larger quantities of air should be removed. To avoid shearing off and embolizing small pieces of the Teflon catheter, never withdraw the metal needle then replace it in the catheter again.
Additional Resources
Dal common currency video (Youtube)
NEJM (Nov 2008; 17 minutes)
